Gout arthritis and purines – not all purines are equal! It’s not that helpful to avoid all foods with purines as some behave differently than others. Limiting SOME foods that are moderate to high in purines that have been found to affect your uric acid levels may help to avoid flares, so it can be helpful to know what those foods are.
What is the deal with purines and gout?
In the past, doctors would recommend that food high in purines should be avoided to reduce the risk of gout attacks. But more research surfaced, and it turns out that this isn’t entirely necessary. In fact, food and drink make very little difference to your uric acid levels.
The mechanism: Around two-thirds of purines are made by the body from the normal process of dying and renewing cells. Around one-third are from external sources of food and drink. When the body breaks down purines, uric acid is formed which is normally re-absorbed in the body or excreted in urine and faeces.
In people with gout, the body can’t get rid of uric acid very well so uric acid levels in the blood rise. Too much uric acid in the blood can cause crystals to form in joints that can be painful. Hard lumps can form in these joints, called tophi and are usually found in the big toe.
A person’s uric acid level is due to a few factors; genetics, kidney function and being overweight are the biggest contributors. Food and drink consumed only contribute to around 10% of your uric acid level, so diet alone isn’t going to help you manage your gout.
You can’t change your genes, so you may have to take uric acid-lowering medication if you have high levels in your blood. Māori and Pacific people are more likely to have genes that reduce the ability of the kidneys to get rid of uric acid, resulting in high uric acid levels in the blood (serum). If high uric acid levels are untreated, it can lead to permanent damage to your joints and kidneys, putting you at risk for heart disease, kidney disease, and metabolic syndrome. If you have someone in your family who has gout or you are Māori or Pacific, it’s a good idea to ask your doctor about a blood test to check your uric acid levels and you may need to start taking medication. Even when there is no pain, the high levels in the blood are causing damage.
Being a healthy weight is always a good idea, and this is something you can modify, unlike your genetics. Some things to keep in mind if you are embarking on a weight loss journey with gout:
1. Losing weight too quickly can lead to a spike in uric acid levels, approaching weight loss at a slower pace might be more beneficial. Aim to develop healthy eating habits where weight loss is a side effect of lifestyle changes.
2. High-intensity exercise can raise uric acid levels but moderate-intensity exercise does not; so stick to moderate exercise to lessen your chance of attacks.
Consider foods that cause a painful flare when you eat them. Keep a diary of when you have a flare and note what you ate and drank before the flare. You may notice a pattern and be able to identify your trigger. There are some common gout flare-triggers; these are:
- Alcohol, particularly beer
- Sugary food and drink
- Liver
- Meat
- Some seafood
People with Gout Arthritis can continue to eat purine-rich food in small to moderate amounts. People who take uric acid-lowering medication such as Allopurinol or Febuxostat can usually enjoy a balanced diet that includes a small amount of purine-rich foods.
What are purines?
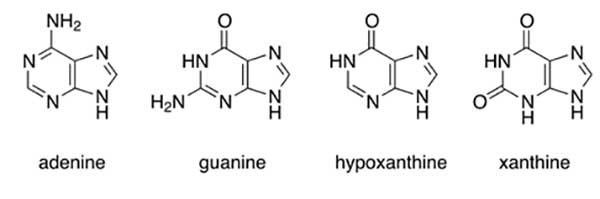
Purines are a class of molecules with two rings and are made up of bases like adenine, guanine (like in DNA and RNA), hypoxanthine, and xanthine.
The type of purine is just as important as the amount of purines. In a review of purine content and the effect on serum uric acid of 270 foods, scientists found that the type of purine and the amount of purines in a food should be taken into consideration in diet therapy for Gout Arthritis.
Foods with a higher ratio of a purine called hypoxanthine (greater than 50%) had more effect on serum uric acid levels than foods with a higher ratio of the purines guanine and adenine. Meat and fish had higher ratios of hypoxanthine and a bigger effect on serum uric acid while other foods studied (cereals, beans, soybean products, seaweeds, dairy products, mushrooms, and vegetables) contained greater than 60% of their total purines as adenine and guanine and did not have an effect on uric acid levels. This demonstrated that it is unnecessary for people with gout to avoid vegetables and grains that are high in purines as there was no detrimental effect on uric acid when consumed.
The review also found that guanine didn’t elevate serum uric acid. Some fish are higher in guanine so don’t have as much effect on serum uric acid. Fish have other nutritional components that are healthy and lower heart disease risk, so shouldn’t be avoided by people with gout because the benefits outweigh the effect on serum uric acid. The review found that oily metallic fish are higher in guanine purines so moderate amounts of these fish are encouraged for people with Gout Arthritis.
Interestingly, chicken, beef and pork liver which have one of the largest effects on uric acid levels are mainly adenine and guanine purines. But the study found that the concentration of purines are so high in liver that an effect was still seen.
Be careful of supplements
Supplements to be wary of include DNA/RNA, chlorella and beer yeast. These are high in purines and could lead to attacks.
The key message for nutrition management of Gout is to look at the overall diet pattern (that’s everything you eat and drink), move towards a healthy eating pattern and maintain a healthy weight.
What is a healthy eating pattern for people with Gout Arthritis?
The Mediterranean diet is one eating pattern that has been associated with a lower risk of Gout Arthritis that you can read more about here.
Some things to consider for a healthy eating pattern:
1. Mainly plant foods. For example, vegetables, legumes, grains, and fruit. These are high in anti-inflammatory compounds such as antioxidants and are nutrient-dense.
2. Wholegrains. For example, oats, wholemeal bread, wheat cereals such as weetbix, wholemeal flour, brown or coloured rice, buckwheat, unhulled barley, quinoa, and bulgur wheat. When choosing bread, check the ingredients list for the word ‘whole’.
3. Low saturated fat. Saturated fat is found in high quantities in food from animals, such as poultry, meat and dairy, and plant sources such as coconut products and palm oil.
4. Omega 3s are part of a healthy eating pattern that lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease and promotes healthy brain function. DHA and EPA are the best omega 3s, ALA is another omega 3 in food that your body can turn into EPA and DHA. Individual rates of conversion vary, so direct sources of EPA and DHA in the diet are best. Seafood such as fresh and canned tuna, herring, mackerel, and salmon are great sources of EPA and DHA. Walnuts, chia seeds, and ground flaxseed are good sources of ALA. You can also buy fish oil and microalgae (for the plant-based people) supplements to help achieve your intake of EPA and DHA. People with Gout Arthritis don’t have to stay entirely away from seafood and shouldn’t.
5. Limit sodium (salt) by reading labels. Sodium is included on the nutrition information panel of packaged foods. Choosing packaged foods with the lowest amount of sodium is one of the best ways you can reduce sodium in your diet. Also, try to cook without salt, so your meal is healthier by default. Then only add salt for taste to your food when you are at the table if absolutely necessary. High blood pressure is another risk factor for gout and having too much sodium (salt) can increase your blood pressure.
6. Low-fat dairy contains purines but dairy proteins appear to lower uric acid levels. Low-fat dairy products are part of a healthy diet for those with Gout Arthritis.
7. Drink water. Water is part of every healthy diet and will help your kidneys in their job to clear excess uric acid. Dehydration can cause uric acid levels to rise, so make sure you are drinking enough water, especially when exercising, using a sauna, or in hot temperatures.
Purine content of some foods
| Very Low | Low | Moderate | High | Very High |
|
Chicken breast, skin, wing. Duck |
Chicken liver | |||
|
Corned beef Bacon Ham |
Beef brisket, shoulder, ribs. Mutton |
Beef tenderloin, tongue, topside, shin. Pork chops Salami Prosciutto |
Beef liver Pork liver |
|
|
Mackerel Salmon Tuna Flounder Oyster Kina Haddock Caviar Rainbow trout |
Bonito Sardine Anchovies
|
For more on a healthy diet:
– How to Get Started – Nutrition and Arthritis
For more about Gout:
– Gout Arthritis – Arthritis New Zealand
– Gout (mate waikawa kai kōiwi) | Health Navigator NZ
– Change_your_life_gout_booklet_2022.pdf (arthritis.org.nz) – Ministry of Health + Pharmac produced booklet
For support from others with Gout, join our Facebook support group:
– Gout Support Group Arthritis NZ | Facebook